
TABLE OF CONTENT
INTRODUCTION: UNLOCKING STRENGTH AND PERFORMANCE
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of creatine, the powerhouse supplement that has revolutionized the fitness landscape. If you’ve ever wondered, “What is creatine?” you’re about to delve into a wealth of information that demystifies this compound and unveils its potential benefits. From debunking myths to understanding optimal dosage and discovering who can benefit, this blog post serves as your guide to harnessing the full power of creatine. Whether you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or someone embarking on a wellness journey, join us on this informative journey into the world of creatine and discover how it can elevate your strength and performance to new heights.
Ikaria Lean Belly Juice is a powerful new formula that makes weight loss easier, faster and much more fun…
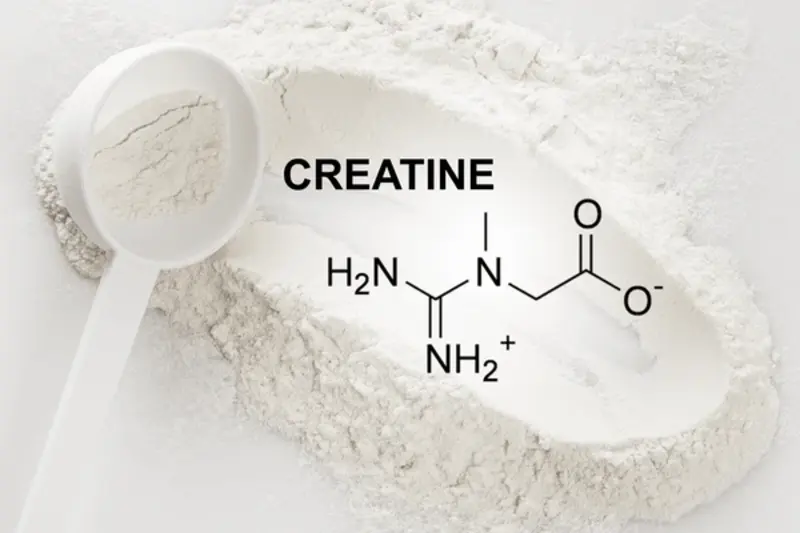
DEFINING CREATINE
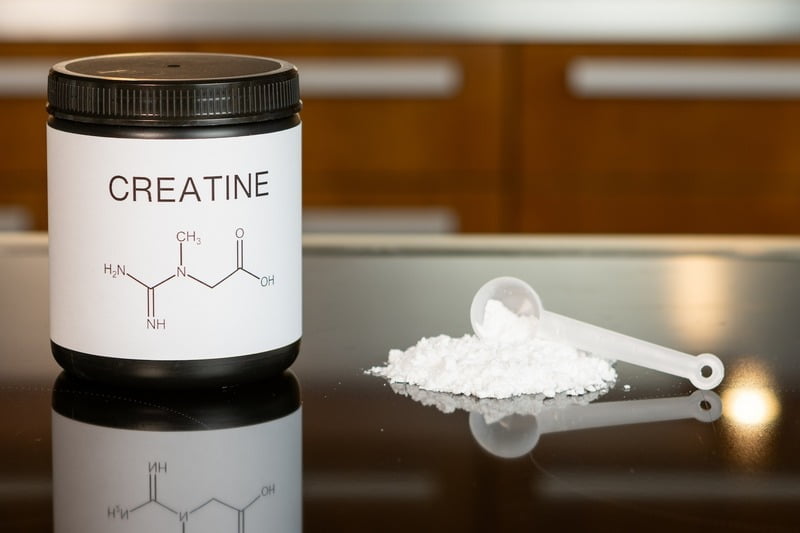
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that plays a pivotal role in the energy production processes within our bodies, particularly during high-intensity activities. Found in small amounts in certain foods and produced by the body, creatine is a powerhouse that fuels our muscles during demanding physical efforts.

To put it simply, creatine acts as a rapid energy reserve, providing the necessary fuel for short bursts of intense activity, such as weightlifting or sprinting. This natural compound is stored in our muscles and used when quick bursts of energy are required.
How Creatine Works: When we engage in activities that demand rapid bursts of energy, like lifting heavy weights or sprinting, our muscles tap into the stored creatine phosphate to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of our cells. This process allows our muscles to perform at their peak for short durations.
Creatine in Foods: While creatine is found in trace amounts in some foods, its concentration is highest in meat and fish. Beef, pork, and certain types of fish, like salmon and tuna, are particularly rich sources of creatine. However, the amounts obtained through diet alone may not be sufficient for individuals engaged in intense physical activities.
Creatine Supplements: Recognizing the performance-enhancing benefits of creatine, many athletes and fitness enthusiasts turn to creatine supplements. These supplements provide a concentrated dose of creatine, ensuring that the muscles have an ample supply for optimized performance.
Why Creatine Matters: Creatine is not just a buzzword in the fitness world; it’s a scientifically proven aid for enhancing strength, increasing muscle mass, and improving overall exercise performance. Numerous studies support its efficacy, making it one of the most researched and trusted supplements in the fitness industry.
UNDERSTANDING CREATINE
Understanding creatine goes beyond recognizing it as a mere energy source; it involves comprehending its vital role in the intricate dance of muscle function and energy metabolism.
The Basics of Creatine: Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that naturally occurs in our bodies. Its primary function revolves around the replenishment of ATP, the cellular fuel that powers muscle contractions during intense, short-duration activities. Picture creatine as the rapid-response team ensuring your muscles have the energy they need precisely when you demand it most.
The Creatine Cycle: During moments of high-intensity effort, like lifting weights or sprinting, our muscles rapidly deplete ATP. Enter creatine phosphate, the stored form of creatine. This compound swoops in to regenerate ATP, allowing the muscle to sustain its power output. This cyclical process enables those short bursts of energy necessary for peak performance.
Natural Creatine Synthesis: Our bodies can synthesize creatine, primarily in the liver and kidneys, using amino acids like glycine, arginine, and methionine. Additionally, we obtain creatine through our diet, with meat and fish being particularly rich sources.
Creatine Supplementation: Recognizing the importance of creatine in optimizing performance, many individuals turn to creatine supplements. These supplements provide a concentrated dose, ensuring that the muscles have an abundant supply for immediate use. It’s a strategic approach for athletes and fitness enthusiasts aiming to enhance their strength, power, and overall exercise performance.
Benefits of Creatine: The benefits extend beyond the immediate energy boost. Creatine supplementation has been extensively researched and linked to increased muscle mass, improved strength, and enhanced recovery between bouts of exercise. These advantages make creatine a go-to supplement for individuals striving for peak physical performance.
In Summary: In essence, understanding creatine involves grasping its dual role as both a natural component of our bodies and a supplement that can be strategically utilized to maximize physical performance. It’s a powerhouse that fuels our muscles during high-intensity activities, ensuring we can push our limits and achieve our fitness goals.
By understanding creatine, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating it into their fitness regimen, harnessing its benefits to elevate their exercise experience. Whether obtained through diet or supplementation, creatine stands as a key player in the pursuit of peak physical performance.
SOURCES OF CREATINE
Understanding the sources of creatine is crucial for those seeking to naturally enhance their levels of this performance-boosting compound. While our bodies can produce creatine, obtaining it from dietary sources plays a significant role in ensuring an ample supply.
Natural Dietary Sources: Creatine is found in varying amounts in a range of foods, with meat and fish standing out as primary sources. Beef, pork, and certain types of fish, such as salmon and tuna, are particularly rich in creatine. Consuming these foods contributes to the overall creatine levels in the body.
Meat as a Creatine Source: Among meat sources, red meats like beef contain higher concentrations of creatine compared to poultry or plant-based options. However, it’s essential to balance dietary choices based on individual preferences and nutritional needs.
Fish as a Creatine Source: Certain fish, especially those with higher fat content, are notable sources of creatine. Salmon, mackerel, and tuna provide not only essential omega-3 fatty acids but also contribute to the body’s creatine stores.
Creatine Content in Various Foods: To give you an idea, a pound of raw beef may contain around 4 to 5 grams of creatine, while a pound of fish can range from 4 to 8 grams. However, cooking and processing can affect creatine levels, so it’s wise to include a variety of sources in your diet.
Vegetarian and Vegan Considerations: For those following vegetarian or vegan diets, obtaining creatine solely from food sources may be a bit challenging, as plants generally have lower creatine levels. In such cases, creatine supplementation becomes a viable option to ensure an adequate intake.
CREATINE SUPPLEMENTATION
Creatine supplementation has become a cornerstone in the pursuit of maximizing physical performance, offering a convenient and effective way to elevate creatine levels in the body.
The Purpose of Creatine Supplements: Creatine supplements are designed to provide a concentrated dose of creatine, ensuring that muscles have an immediate and abundant supply during high-intensity activities. This strategic approach helps optimize energy production, allowing individuals to push their limits and achieve peak performance.
Types of Creatine Supplements: Several types of creatine supplements are available, with two main variants coming into focus: creatine monohydrate and creatine hydrochloride (HCL). Each has distinct characteristics that cater to different preferences and needs.
- Creatine Monohydrate: Creatine monohydrate, composed of creatine paired with a water molecule, stands out as the most researched and cost-effective option. Renowned for its effectiveness in increasing muscle creatine stores, it remains a popular choice for those seeking reliable results without a hefty price tag.
- Creatine Hydrochloride (HCL): Creatine hydrochloride, formed by binding creatine with hydrochloric acid, offers enhanced solubility compared to monohydrate. This solubility advantage may appeal to individuals experiencing digestive discomfort with creatine monohydrate. HCL also often requires a lower dosage, making it a concentrated option for those seeking efficiency.
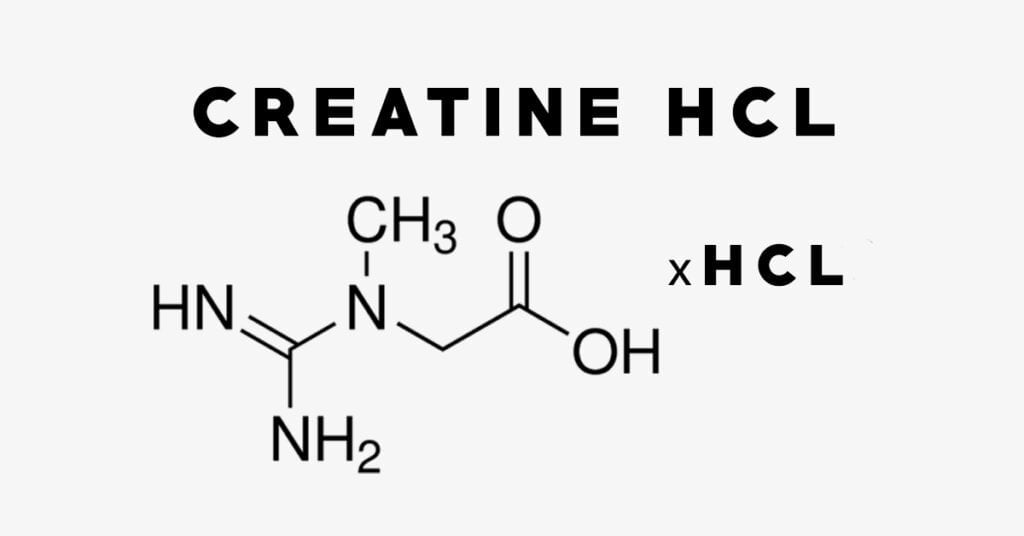
- Choosing Between the Two: The choice between creatine monohydrate and HCL often hinges on personal preferences. If solubility and lower dosages are priorities, HCL might be the preferred option. However, for those valuing cost-effectiveness and a well-established track record, creatine monohydrate remains a reliable and budget-friendly choice.
Conclusion: Both creatine monohydrate and creatine hydrochloride are effective supplements for enhancing physical performance. Your decision should align with personal preferences, digestive considerations, and budget constraints. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before introducing any new supplement to ensure it complements your specific health needs.
Loading and Maintenance Phases: For those new to creatine supplementation, a loading phase involving higher initial doses can help saturate muscle creatine stores more rapidly. This is typically followed by a maintenance phase where a lower daily dose is sufficient to sustain elevated creatine levels.
When to Take Creatine: Creatine supplements are versatile regarding timing. Whether taken before or after a workout or even spread throughout the day, the key is consistency. What matters most is maintaining a regular intake to ensure a continuous supply of muscle energy production.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation: The benefits of creatine supplementation are well-established through extensive research. These include increased muscle strength, enhanced power output, and improved overall exercise performance. Additionally, creatine has shown potential benefits for recovery between bouts of exercise.
Safety and Considerations: Creatine supplementation is generally considered safe for healthy individuals when used as directed. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, especially for those with pre-existing medical conditions.
Choosing a Quality Supplement: When selecting a creatine supplement, opt for reputable brands to ensure product quality and purity. Look for products with minimal additives or fillers, and consider reviews or recommendations from trusted sources.
BENEFITS OF CREATINE
The benefits of creatine extend far beyond its role as a quick energy source during intense workouts. Widely researched and endorsed by fitness enthusiasts, creatine supplementation has been linked to increased muscle strength, enhanced power output, and improved overall exercise performance. Not limited to immediate gains, creatine has demonstrated its effectiveness in supporting muscle growth and expediting recovery between workout sessions. Its positive impact on high-intensity activities makes creatine a go-to supplement for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike. As a natural and evidence-backed aid, creatine stands as a valuable addition to a well-rounded fitness regimen, contributing to the pursuit of peak physical performance.
MYTHS AND MISCONCEPTIONS ABOUT CREATINE
Despite its well-established benefits, creatine is not immune to myths and misconceptions circulating in the fitness community. Let’s debunk some of the most common misunderstandings to provide a clearer understanding.

Myth 1: Creatine is a Steroid Reality: Creatine is not a steroid. It’s a naturally occurring compound found in our bodies and certain foods. Unlike steroids, creatine doesn’t interfere with hormone levels or pose the associated risks.
Myth 2: Creatine is Only for Bodybuilders Reality: Creatine benefits a wide range of individuals, not just bodybuilders. Athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone engaging in high-intensity activities can leverage creatine for improved strength, power, and exercise performance.
Myth 3: Creatine Causes Kidney Damage Reality: Numerous studies refute the idea that creatine harms kidneys in healthy individuals. When used as recommended, creatine supplementation is generally safe. However, those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult a healthcare professional before considering supplementation.
Myth 4: Creatine Causes Dehydration and Muscle Cramps Reality: Creatine doesn’t cause dehydration or muscle cramps when consumed in appropriate doses. Creatine may enhance hydration levels within muscle cells, contributing to improved exercise performance.
Myth 5: Creatine is Only Effective with High Doses Reality: Creatine is effective even at lower, maintenance doses. While some may opt for a loading phase with higher initial doses, research indicates that consistent, lower doses can achieve the desired results over time.
Myth 6: Creatine is Only for Younger Individuals Reality: Creatine benefits individuals of various ages. Older adults, in particular, may experience improved muscle strength and functional capacity with creatine supplementation, contributing to overall well-being.
Understanding these myths helps separate fact from fiction, ensuring that individuals make informed decisions about incorporating creatine into their fitness routines. As with any supplement, it’s crucial to rely on evidence-based information and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Creatine, when used responsibly, emerges as a valuable and safe tool for optimizing physical performance.
DOSAGE AND TIMING OF CREATINE SUPPLEMENTATION
Understanding the optimal dosage and timing of creatine supplementation is key to maximizing its benefits. Here’s a concise guide to help you navigate these crucial aspects.
Dosage: The consensus among experts is that a creatine “loading phase” is not mandatory. However, for those looking to saturate their muscle creatine stores more rapidly, a common loading dose is 20 grams per day (divided into 4 doses) for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day. For those opting to skip the loading phase, starting with a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day is sufficient to gradually elevate and sustain creatine levels.
Timing: The timing of creatine intake is flexible, with studies showing benefits regardless of when it’s consumed. Some prefer taking creatine pre-workout to ensure elevated levels during exercise, while others opt for post-workout to aid in recovery. Alternatively, spreading the dose throughout the day can maintain a consistent creatine supply.
Combining with Food: Creatine can be taken with or without food, as its absorption is not significantly affected by food intake. However, combining it with a source of carbohydrates and protein may enhance creatine uptake by muscle cells.
Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial when supplementing with creatine. Adequate water intake helps support its effectiveness and may prevent potential side effects like cramping.
Individual Considerations: Individual responses to creatine can vary. Factors such as body weight, muscle mass, and overall fitness goals may influence the ideal dosage. It’s advisable to start with a conservative dose and adjust based on individual tolerance and preferences.
Consistency is Key: Whether you choose a loading phase or opt for a maintenance dose, consistency is paramount. Regular and steady intake ensures a sustained elevation of creatine levels in the muscles, contributing to optimal performance over time
WHO CAN BENEFIT FROM CREATINE
Creatine is a versatile supplement that extends its benefits to a broad spectrum of individuals, beyond the confines of professional athletes. Here’s a concise breakdown of who can reap the advantages of incorporating creatine into their fitness routine.
Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts: Creatine is a game-changer for athletes engaging in high-intensity, short-duration activities. From sprinters to weightlifters, enhanced energy production and improved muscle performance can lead to better results and achievements.
Bodybuilders: For those sculpting their physique through resistance training, creatine aids in muscle growth, strength gains, and faster recovery between intense workout sessions. It complements the demands of progressive resistance training programs.
Older Adults: Creatine isn’t reserved for the young and athletic. Older adults can benefit from creatine supplementation, experiencing improvements in muscle strength and functional capacity. This can contribute to maintaining an active and independent lifestyle.
Vegetarians and Vegans: As creatine is primarily found in meat and fish, individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets may have lower natural creatine intake. Creatine supplementation becomes particularly beneficial for this demographic, ensuring they still enjoy the performance benefits associated with creatine.
Those with Physically Demanding Jobs: Individuals with physically demanding occupations that involve repetitive, high-intensity tasks can also benefit from creatine. The improved energy production and muscle support can enhance endurance and reduce the risk of fatigue.
Anyone Pursuing Fitness Goals: Whether you’re aiming for weight loss, overall fitness, or simply looking to optimize your physical performance, creatine can be a valuable addition. Its benefits extend to a wide range of fitness goals, making it a versatile and accessible supplement.
Consultation and Considerations: Before incorporating creatine, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for those with pre-existing medical conditions. Additionally, considering individual fitness goals and preferences can help tailor creatine supplementation to specific needs.
CONCLUSION: MAXIMIZING THE BENEFITS OF CREATINE
Creatine stands out as an accessible ally for a diverse range of individuals. From athletes seeking podium finishes to older adults aiming for vitality, the advantages of creatine are expansive and well-documented.
Understanding fundamental aspects such as the different types of creatine supplements, debunking myths, and grasping optimal dosage and timing empowers individuals to make informed decisions tailored to their unique needs. Creatine’s ability to enhance strength, power, and overall exercise performance has solidified its place as one of the most researched and respected supplements in the fitness world.
You must understand it’s crucial to recognize creatine’s inclusivity. It’s not reserved for a select few; rather, it extends its benefits to athletes, bodybuilders, older adults, and even those with physically demanding jobs. The key lies in a thoughtful approach, consulting with professionals, and understanding individual requirements.
Your journey to peak physical excellence awaits – fueled by the science-backed prowess of creatine. READ MORE




Pingback: MEN AND RED MEAT: A BALANCED APPROACH TO HEALTH AND NUTRITION